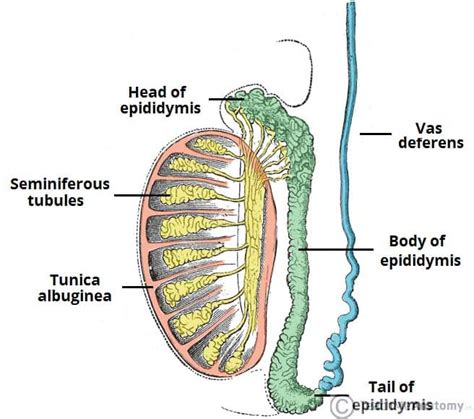
testes secretes a thick alkaline fluid|14.2: Anatomy and Physiology of the Male Reproductive System : convenience store The testes are the site of sperm production and hormone synthesis, while the epididymis has a role in the storage of sperm. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the testes and epididymis – their structure, .
A score of >8 is strongly predictive of necrotizing fasciitis (positive predictive value, 93.4%; 95% CI, 85.5–97.2). Criticisms & Further Discussion Prior to derivation of the LRINEC score, the admission WBC > 15.4 x 10(9)/L or serum sodium [Na] < 135 mmol/L) was suggested as a method for distinguishing between patients with NF and nonnecrotizing .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da NATIVO_AGROFIT_BULA_02.02.2022 NATIVO VERIFICAR RESTRIÇÕES DE USO CONSTANTES NA LISTA DE AGROTÓXICOS DO ESTADO DO PARANÁ Registrado no Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento/MAPA sob nº 00205 COMPOSIÇÃO: methyl(E) .
2,422 solutions. Terms in this set (15) prostate gland. gland under the bladder and surrounds the end of urethra; during ejaculation secretes a thick, alkaline fluid into the semen that aids motility of sperm. phimosis. narrowing of foreskin so that it cannot be retracted to expose the glans . Introduction. The male reproductive system consists of the internal structures: the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, prostate, and the external structures: the scrotum and penis. About the size of a walnut, the prostate is formed of both muscular and glandular tissues. It excretes an alkaline, milky fluid to the passing seminal fluid—now called .Leydig cells in the testes secrete testosterone under the control of luteinizing hormone (LH) from the pituitary gland. Testosterone is needed for male sexual development at puberty, and to maintain normal spermatogenesis after puberty.
It secretes a thin, alkaline fluid that adds protection to the sperm from being immobilized by the low pH level of the urethra. The urethra passes through its center like a doughnut. Bulbourethral Glands The testes are the site of sperm production and hormone synthesis, while the epididymis has a role in the storage of sperm. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the testes and epididymis – their structure, . Fluid secreted by the seminal vesicles into the ducts makes up about 70 percent of the total volume of semen, which is the sperm-containing fluid that leaves the penis during an ejaculation. The fluid from the seminal . Testes. The testes (singular = testis) are the male gonads —that is, the male reproductive organs. They produce both sperm and androgens, such as testosterone, and are active throughout the reproductive lifespan of the .
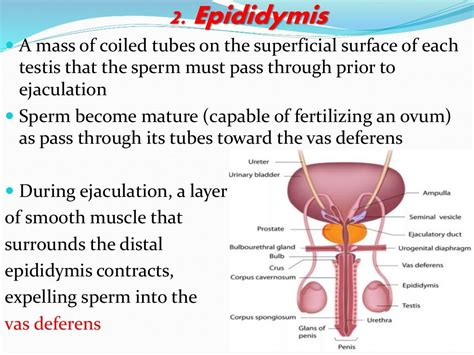
Fluid secreted by the seminal vesicles into the ducts makes up about 70 percent of the total volume of semen, which is the sperm-containing fluid that leaves the penis during an ejaculation. The fluid from the seminal .connect the epididymis and the urethra and serves as the excretory ducts for the testes. Urethra. . Vesicles. secretes fluids which nourish the sperm and increase their mobility and makes up part of the semen. Prostate Gland. secretes a milky alkaline fluid into the semen increasing the mobility of sperm. Penis. discharges urine and semen .Unique for its role in human reproduction, a gamete is a specialized sex cell carrying 23 chromosomes—one half the number in body cells. At fertilization, the chromosomes in one male gamete, called a sperm (or spermatozoon), combine with the chromosomes in one female gamete, called an oocyte. The function of the male reproductive system is to produce sperm .sac in which testes are suspended, hang underneath penis outside male's body. . thick whitish fluid ejaculated from the penis (about 3.5 ml per ejaculation). Can contain as many as 400 million sperm plus secretions from the prostat, Cowper's and seminal vesicles. . Secretes a milky alkaline fluid that helps sperm survive in the acidic .
Once in the ejaculatory duct, the semen passes through the prostate, which secretes an alkaline fluid that helps thicken the semen so sperm can better stay within the female reproductive system. The semen then passes the bulbourethral glands or Cowper’s glands, which release a thick fluid that lubricates the urethral opening and clears the . Semen, fluid that is emitted from the male reproductive tract and that contains sperm cells, which are capable of fertilizing the female’s eggs. Semen also contains liquids that combine to form seminal plasma, which helps keep the sperm viable. In the sexually mature human male, sperm cells are produced by the testes.
These vesicles secrete their fluid contents in the ejaculatory tract. Fluid from seminal vesicles is thick. It contains fructose, citric acid, proteins, potassium, inorganic phosphorus, and prostaglandins. When the fluid combines with sperm in the ejaculatory duct, the fructose becomes the primary source of energy for the sperm outside a man . Primitive gonads become testes; other tissues produce a penis and scrotum in males. . is an exocrine gland which secretes a clear fluid known as pre-ejaculate that is generated upon sexual arousal. This gland releases its secretion prior to the release of the bulk of the semen. . The seminal vesicles produce a thick fluid that is alkaline .Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like What are the male and female gonads?, In the formation of the germ cells, the specialized cell division process is known as:, Which gland secretes a thin, milky, alkaline fluid that enhances sperm motility? and more.A and P test 3. 50 terms. picking_berries. Preview. Biol 2401 Final Exam. 306 terms. anniekrivera. Preview. . produces fluid for semen alkaline secretions neutralize acidic secretions of vagina & epididymis. bulbourethral gland. male reproductive; secretes lubricating fluid to facilitate insertion of penis into vagina. penis. male .
Cowper’s glands secrete a thick, alkaline fluid. When the vasa deferentia travel through the center of the prostate gland, each widens to form the ampulla of the ductus. It is here that the seminal glands empty their contents. . The testes contain Sertoli cells that secrete spermatid carrier fluid, as well as Leydig cells that produce .also known as testes, are the two small, egg-shaped glands that produce the sperm (singular, testis). These glands develop within the abdomen of the male fetus and normally descend into the scrotum before or soon after birth. . During ejaculation, the prostate gland secretes a thick, alkaline fluid into the semen that aids the motility of the .The final secreted fluid in the prostatic urethra is now called semen, which helps sperms pass farther into the female reproductive tract. . a blood test, and a rectal exam that allows physicians to palpate the prostate and check for unusual nodular masses. If a mass is detected, the cancer diagnosis is confirmed by a biopsy of the cells .
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Testes, Scrotum, Seminal fluid and more. . thick, whitish fluid consisting of sperm and secretions from several glands of the male reproductive tract . glands in males that secrete a viscous fluid that provides nutrition to the sperm cells. Prostate gland. gland in males that .During ejaculation the prostate gland secretes a thick alkaline fluid into the semen that aids the motility of the sperm. Motility. means ability to move. Cryptorchidism. known as an UNDESCENDED TESTICLE , is a developmental defect in which one or both of the testicle fail to descend into their normal position in the scrotum. crypt/o. hidden .The external sac that contains the testes is called the. scrotum. Fluid containing sperm and secretions from the male reproductive glands is called. semen. . Which structure at the base of the bladder secretes a thin alkaline fluid that protects sperm from an acidic environment? prostate. Which of the following terms refers to the prepuce?
It secretes a thin, alkaline fluid that adds protection to the sperm from being immobilized by the low pH level of the urethra. The urethra passes through its center like a doughnut. Bulbourethral Glands . Also called as Cowper’s gland, these glands also secrete alkaline fluid to counteract the acidic environment in the urethra.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Function of Reproductive Organs, Testes, Anatomy of a Testis and more. . lateral to each vas deferens on posterior bladder wall secrete alkaline fluid that contains fructose (energy for sperm) & prostaglandins (promotes muscular contractions in female reproductive tract) Stores and secretes a clear, slightly alkaline fluid constituting up to one-third of the volume of semen. Raise vaginal pH.(25-30% of semen) Scrotum Pouch of skin and muscle that holds testicles. Regulates temperature at slightly below body temperature. Semen Usually white but can be yellow, gray or pink (blood stained).secretes a thick, yellowish fluid into the ejaculatory duct, fluid secreted comprises about 60% of semen, secreted fluid contains fructose as well as other substances that nourish sperm and help ensure mobility. . secretes thin, milky, alkaline fluid into urethra. . Sac of tissue in which the testes lie? scrotum. another name for foreskin .
mts c45 universal testing machine
On a microscopic level, the inner lining of the seminal vesicles is extensively folded, and is made up of epithelial cells, which secrete the sugars, proteins, and mucus that contribute to seminal fluid. The outside of the vesicles are lined by a coat of smooth muscle, which can contract during ejaculation.Test. Expert Solutions. Q-Chat. Live. Blast. Categories. Checkpoint. Exams. . secretes alkaline fluid with nutrients, prostaglandins, and a coagulating enzyme that support sperm, enhance their motility, and maintain semen in the female reproductive tract after ejaculation. Prostate gland.The two testes (singular, testis) are sperm– and testosterone-producing gonads in male mammals, including male humans.These and other organs of the human male reproductive system are shown in Figure 18.3.2. The testes are contained within the scrotum, a pouch made of skin and smooth muscle that hangs down behind the penis.. Figure 18.3.2 The male .
Testicles (testes). These are two oval-shaped organs that make male sex cells called sperm after puberty. . Located at the base of the bladder, the two seminal vesicles secrete a thick fluid that nourishes the sperm. The bladder is the muscular sac that stores urine (pee) until it is released through the urethra.serves as a storage site for sperm cells and as the excretory duct of the testes. seminal vesicles. produce secretions to nourish and protect sperm on their journey through the female reproductive system. . secretes a thin, milky alkaline fluid that enhances sperm motility. Epididymis. connected by the efferent duct of each testis.
This is part of my test on chapters 42 and 43. Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. . located below the bladder, which secretes an alkaline fluid that neutralizes the acids in the female reproductive system. Bublourethral glands. secrete an alkaline fluid which neutralizes traces of acidic urine in the urethra. Semen.
The Testes and Epididymis
Physiology, Male Reproductive System
Male Reproductive System Anatomy and Physiology
WEBTwitter動画(ランキング). みんながダウンロード保存した人気のツイッター動画. 24時間. 3日間. 1週間. 不正なビデオリンクの通報・削除のリクエストは24時間以内に処理され .
testes secretes a thick alkaline fluid|14.2: Anatomy and Physiology of the Male Reproductive System